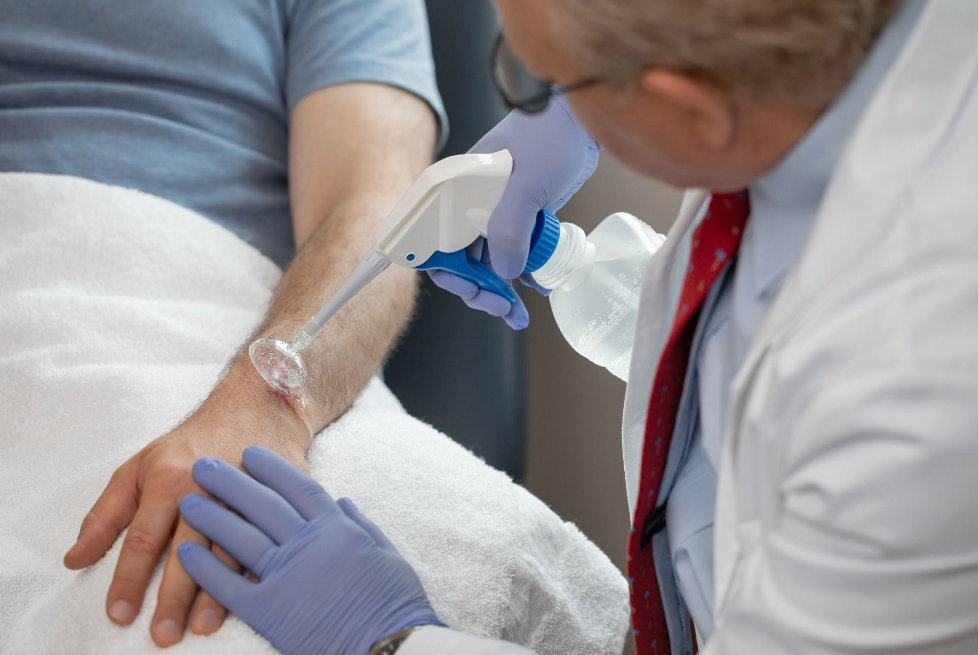
When it comes to wound care, thorough cleansing is a crucial step in the healing process. Wound irrigators play a significant role in facilitating effective wound cleansing by providing a controlled stream of fluid to remove debris, bacteria, and other contaminants. Let’s delve into the world of wound irrigators and explore how they enhance wound care with advanced cleansing.
What is a Wound Irrigator?
A wound irrigator, also known as a wound flusher or wound lavage system, is a medical device specifically designed to deliver a controlled stream of fluid to cleanse wounds. It typically consists of a handheld device with a nozzle that allows for precise and targeted irrigation. The fluid used can vary and may include sterile saline solution, antiseptic solutions, or wound cleansers.
Enhancing Wound Cleansing
They are designed to enhance the process of wound cleansing in several ways
Debris and Contaminant Removal: The controlled stream of fluid from the wound irrigator helps dislodge and remove debris, bacteria, and foreign particles from the wound bed. This helps reduce the risk of infection and promotes a clean environment for healing.
Promoting Granulation Tissue Formation: Effective wound cleansing with it can promote the formation of granulation tissue, which is essential for wound healing. By removing necrotic tissue and promoting a clean wound bed, the irrigator supports the growth of healthy tissue.
Facilitating Dressing Application: Proper wound cleansing with it prepares the wound bed for the application of dressings. By removing excess exudate and debris, the irrigator allows dressings to adhere securely and provides an optimal environment for healing.
Appropriate Usage and Considerations
Healthcare professionals should consider the following:
Education and Training: Healthcare professionals should receive appropriate education and training on the correct usage of wound irrigators to ensure optimal outcomes and patient safety.
Selection of Irrigation Solution: The choice of irrigation solution should be based on the individual patient’s needs, wound characteristics, and the healthcare provider’s recommendations.
Irrigation Technique: Healthcare professionals should follow appropriate techniques for wound irrigation, including maintaining the proper distance from the wound, adjusting the pressure of the irrigation stream, and ensuring adequate coverage of the wound bed.
Sterility and Infection Control: Maintaining sterility and adhering to infection control measures during wound irrigation is crucial to prevent the introduction of further contamination.
Conclusion
By incorporating the use of a wound irrigator into wound care protocols, healthcare professionals can enhance wound cleansing, promote faster healing, and improve patient outcomes. The precise and controlled delivery of fluid provided supports effective wound management, ensuring that wounds receive the thorough cleansing they require for optimal healing.